What Takes Place In Your Body When You Consume Too Much Sugar?
People are unaware that there are numerous hidden sources of sugar that they consume in addition to white sugar.


People don't even realize it, but there are many hidden sources of sugar that they consume in addition to white sugar. One teaspoon of ketchup, for example, contains one teaspoon of sugar. According to the FDA, your daily sugar intake should not exceed 10% of your total calorie intake.
WHO recommends no more than 6 teaspoons of sugar, or 25 grams, for an adult with a normal BMI (Body Mass Index).
There are numerous myths about the effects of sugar on our health. Despite the fact that humans require glucose to survive, it's no secret that the excessive amounts of sugar found in everyday foods such as processed snack foods, canned food, and soft drinks have become too much for our bodies to handle.
Is all sugar harmful?
Fruit contains naturally occurring sugar, but it also contains a plethora of other nutrients and fiber, distinguishing it from added fructose in soda or sugar-sweetened cookies and cakes. Sugar-sweetened foods frequently lack essential nutrients. Although eating naturally occurring sugar is healthier and safer, some people, such as diabetics, may also need to limit their intake of this type of sugar.

This is what happens in your body when you consume sugar, from gaining weight to an increased risk of diabetes later on:
- Gaining Weight
When you consume more sugar than your body can use, it converts it into fatty acid and stores it in adipose fatty cells such as the hips, thighs, arms, and stomach for later use.

2. Pre-Diabetes
When you eat anything that contains glucose or basic carbohydrate building blocks, your body will release insulin because insulin is what helps your body convert glucose into energy.
With insulin resistance, your body is unable to absorb glucose quickly enough, causing glucose to accumulate in your bloodstream and liver. This, when combined with the appropriate genetic and environmental factors, can result in pre-diabetes and, eventually, diabetes.
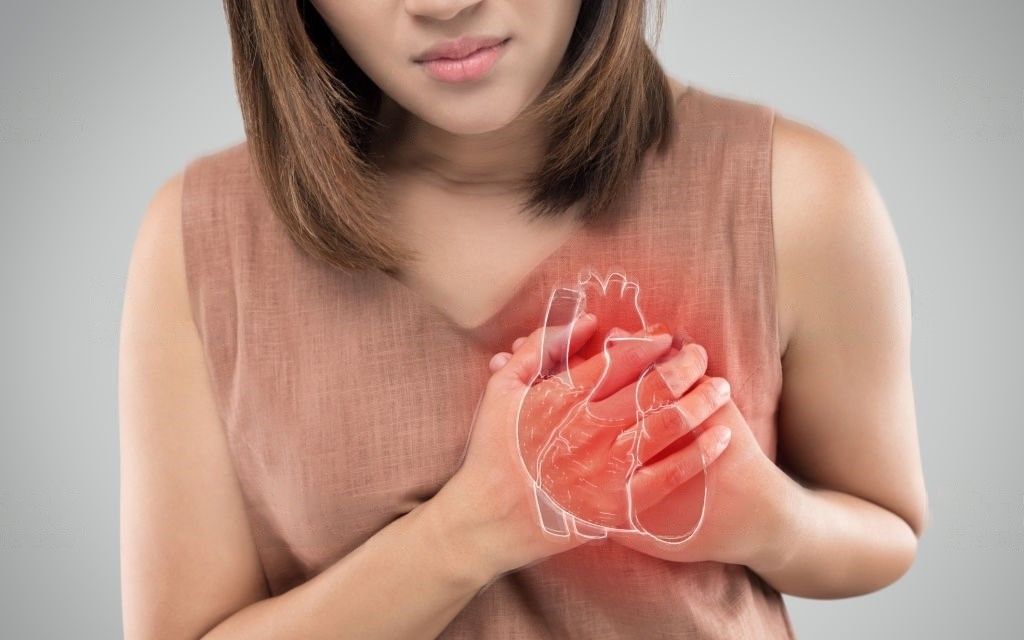
3. Cardiovascular Disease
The most obvious physical symptom of consuming too much sugar is weight gain, but alarming research shows that even if you're not overweight, a sugar-rich diet can significantly increase your risk of cardiovascular disease.

4. Dementia or Memory Loss
Excess sugar is well known to be harmful to our health in terms of diabetes and obesity, but this potential link with Alzheimer's disease is yet another reason why we should limit our sugar intake in our diets.

5. Anxiety and Depression
Sugar causes inflammation all over the body, including the brain.
Creating a link, a sugary diet can cause an inflammatory response in your body, leading to increased stress, anxiety, and even depression.

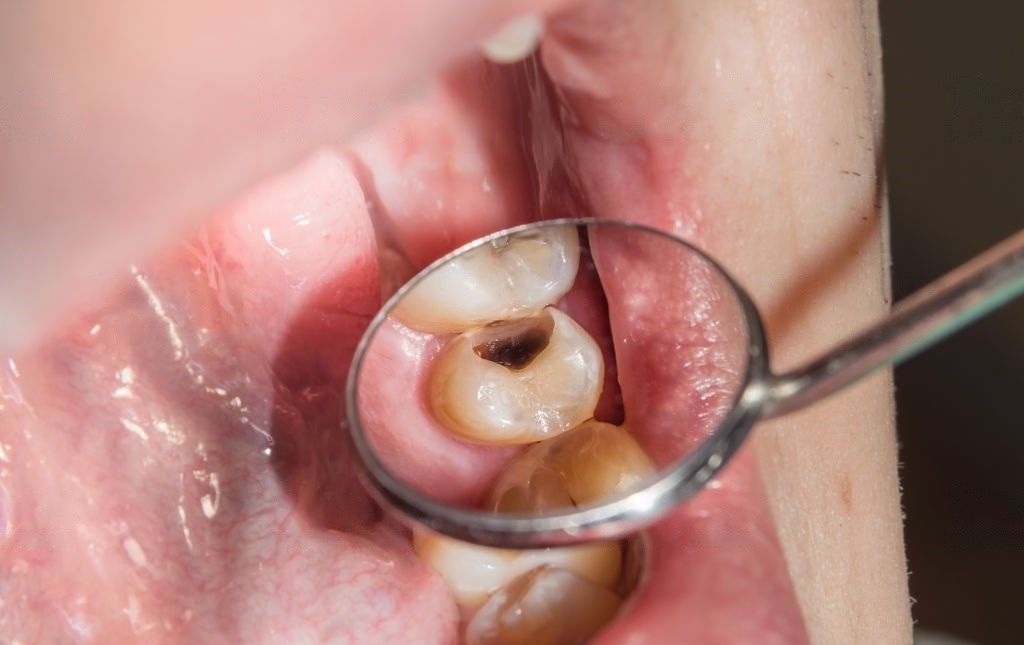
6. Caries of the Teeth
Contrary to popular belief, sugar does not cause cavities. Cavities are caused by the waste product (acid) produced by sugar interacting with the surface of your teeth. So, if you don't watch what you eat (or ignore regular dental cleanses), you might end up with a mouth full of disintegration.
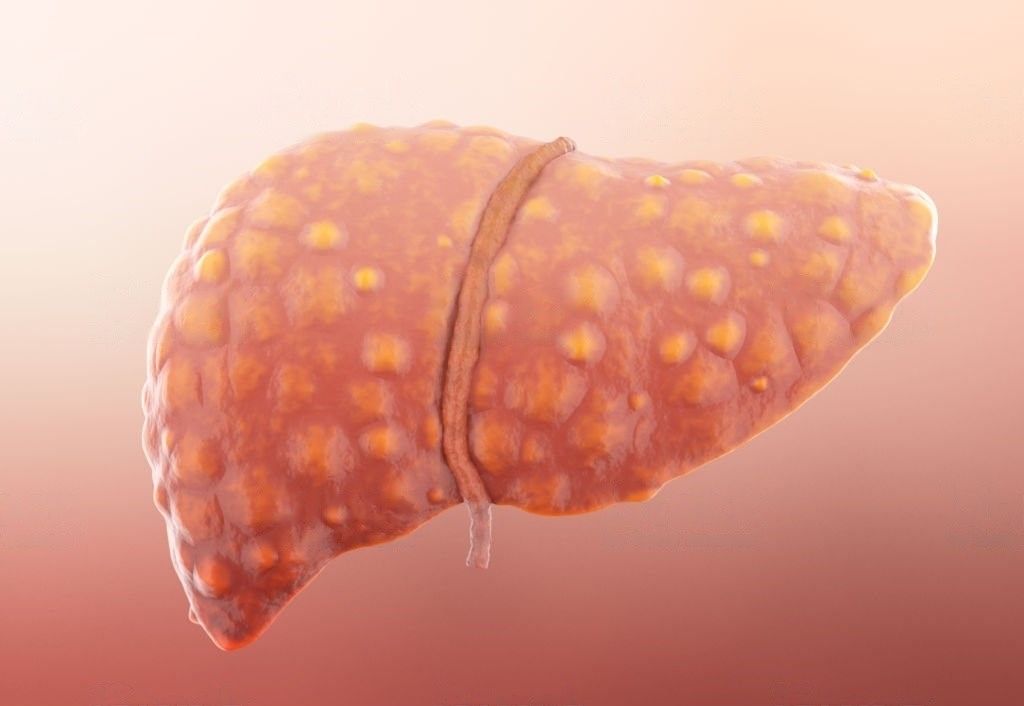
7. Liver Damage
According to some researchers, fructose, like alcohol, can cause fatty liver or cirrhosis. Fructose is the sugar that gives the fruit its sweetness. Simply eating fruit will not harm your liver. Consuming canned or processed fruit or fruit-based products with high levels of added fructose, on the other hand, can cause liver damage.
SUMMARY
Too much added sugar has a number of negative health effects, including fatigue and weight gain, as well as more serious conditions such as heart disease. Many processed foods and beverages contain added sugars.
People can cut their sugar intake by learning what to look for on food labels, avoiding or reducing common sugar sources like soda and cereal, and prioritizing unprocessed whole foods.
If a person is concerned about gaining weight, signs of diabetes, or other symptoms that occur after eating sugar, they should consult a doctor.
Jayti Shah is a Clinical Nutritionist with a master's degree in Clinical Nutrition and Dietetics. She is a member of the Indian Dietetic Association (IDA). Over the last 9 years, she has helped 400 clients in their clinical and weight loss journeys. She works with SocialBoat as a nutrition consultant.
At SocialBoat, we offer custom diet plans and guided workouts to help you achieve your goals in a 360-degree approach. Our gamified experience ensures that you don’t find workouts boring and we reward you for being consistent with your efforts.

